Caudal: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19762734/ A comparison of high volume/low concentration and low volume/high concentration ropivacaine in caudal analgesia for pediatric orchiopexy] | [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19762734/ A comparison of high volume/low concentration and low volume/high concentration ropivacaine in caudal analgesia for pediatric orchiopexy] | ||
Fisher QA, Shaffner DH, Yaster M. Detection of intravascular injection of regional anaesthetics in children. Can J Anaesth. 1997 Jun;44(6):592-8. PMID: 9187777 | |||
[https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23144440/ Case report: neurological complications associated with epidural analgesia in children: a report of 4 cases of ambiguous etiologies] | |||
[[TYK5 |Test Your Knowledge]]: newborn spinal cord | [[TYK5 |Test Your Knowledge]]: newborn spinal cord | ||
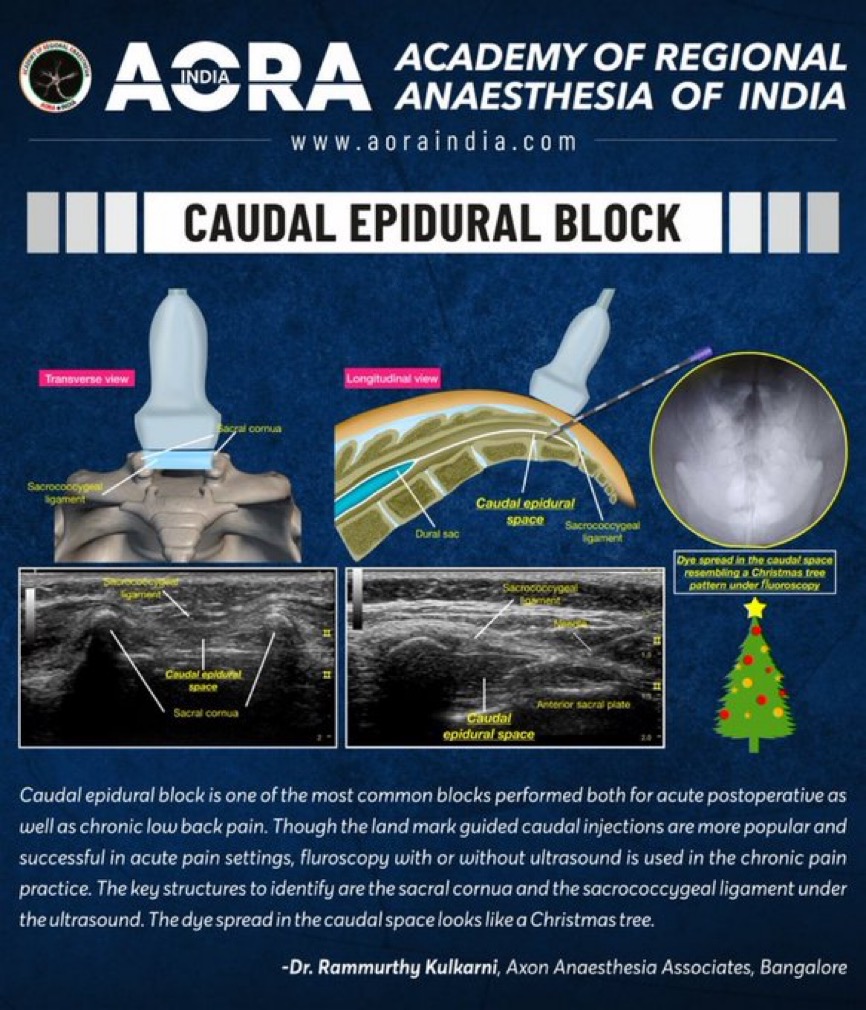
[[File:Caudal-Kulkarni.jpeg]] | [[File:Caudal-Kulkarni.jpeg]] | ||
Revision as of 14:23, 18 July 2023
This is a Stub Notice. This page has not been completed. You can work on this page by signing in and going to the Edit tab. Thanks for helping to make PedsAnesthesia.Net Wiki useful.
Go to the Main Page to see the Topic Outline.
Go to the Generalized Suggested Outline for information on case-specific details for each page.
Go to the Test Page for examples on how to use references in the page.
Relevant Article Depot:
Caudal Epidural Block: An Updated Review of Anatomy and Techniques
Dexmedetomidine as an adjunct for caudal anesthesia and analgesia in children
Caudal anesthesia in pediatrics: an update
The Use of Epinephrine in Caudal Anesthesia Increases Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output in Children
Caudal anesthesia in children with shunt devices
The use of additives to local anaesthetic solutions for caudal epidural blockade
Ultrasound-guided caudal blockade and sedation for paediatric surgery: a retrospective cohort study
Fisher QA, Shaffner DH, Yaster M. Detection of intravascular injection of regional anaesthetics in children. Can J Anaesth. 1997 Jun;44(6):592-8. PMID: 9187777
Test Your Knowledge: newborn spinal cord